what is power transformer, types and applications?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Power transformers are the essential components in electrical systems, used for voltage regulation and efficient power transmission .in this article we explore what is power transformer is its different types and various application across industries, they are a primarily used to step up – or step – down voltage levels without power transformers, electricity transmission over long distances would lead to significant energy losses.
Now, let me drive into the fundamentals of power transformers and how they function.
what is power transformer
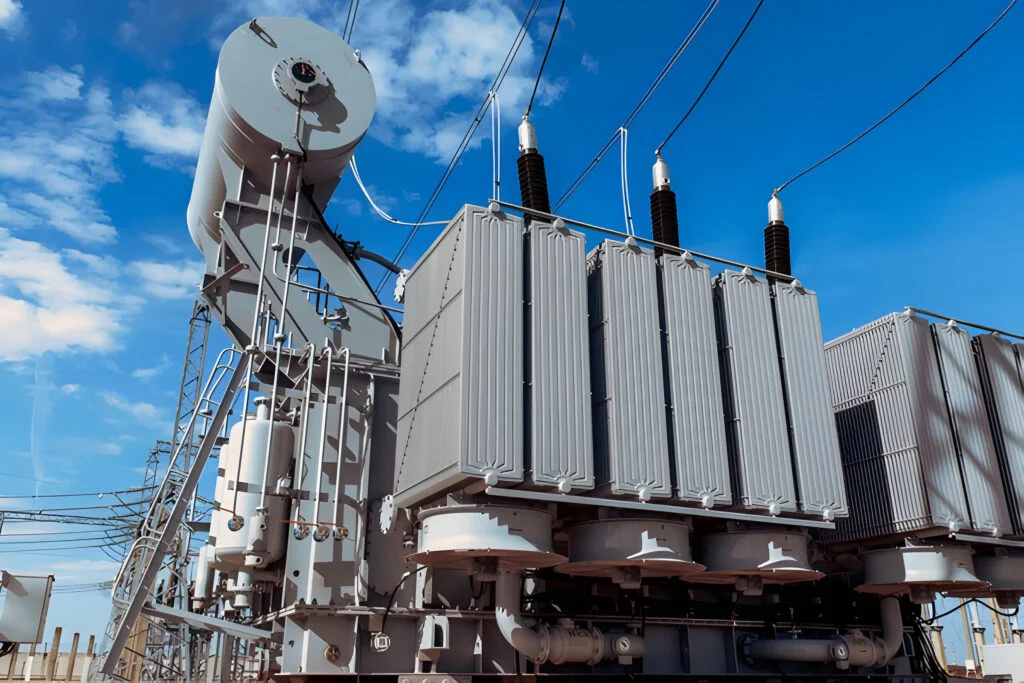
a power transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction .it operates on the principle of faraday’s low of electromagnetic induction, stepping up – or step –down voltage level to ensure efficient power distribution power transformers generated are mainly used high voltage transmission networks where
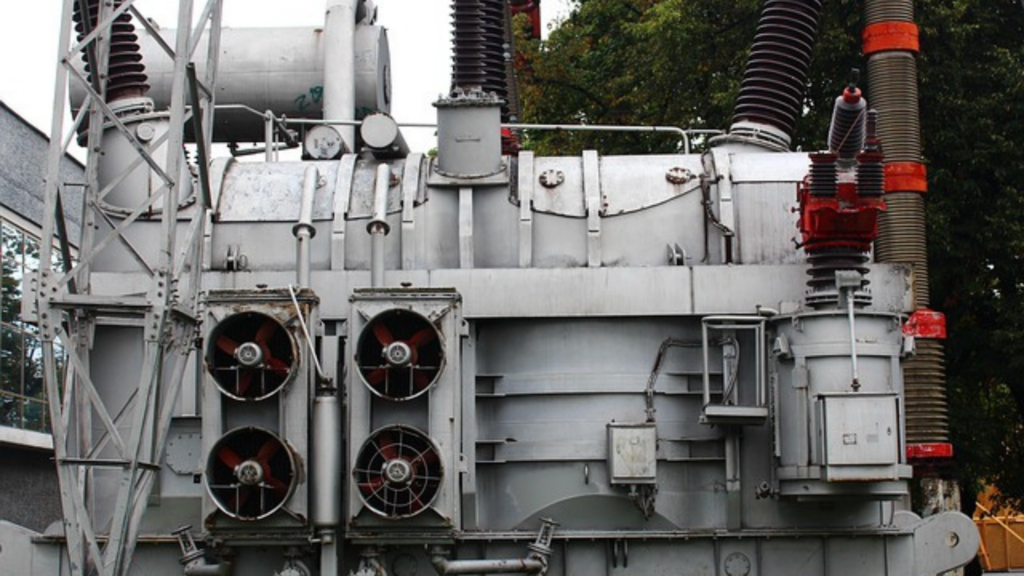
electricity generated at power station needs to be transported efficiently before reaching consumers. They are essential for reducing resistive losses in power lines, making electrical transmission more cost- effective power transformers are classified as static devices because they have no moving part, but they are also passive devices because they do not generate or consume electrical energy, but only transfer it from one circuit to another.
Why are Power Transformers Used?
Power transformer are essential electrical devices to transfer electrical energy between different voltage levels in power system. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction
- Voltage Step –Up and Step Down
- Step –up Transformer: increase voltages for efficient long distance in transmission to reducing energy losses.
- Step Down Transformers: Decrease voltage for safe distribution to homes, business, and industries
- Efficient power Transmission
High voltage transmission reduces current, minimizing resistive losses(I²R losses)
- Electrical Isolation
Isolation transformers protect sensitive equipment by separating primary and secondary circuits preventing electrical shocks and system damage
- Load Distribution
They help in managing electrical loads across power by distributing energy effectively from generation plant to end of users
How does a power transformer work?
A power transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer electrical energy between different voltage level without changing Frequency. Where a changing magnetic field created by an alternating current (AC) in the primary winding induces a voltage in the secondary winding, effectively stepping up down the voltage
Types of power transformer
- Based on voltage
- Step-Up Transformer: Increases voltage for efficient long distance power transmission used in power generation station.
- Step down transformer: reduces voltage for safe distribution homes, business and industries
- Based on core Design
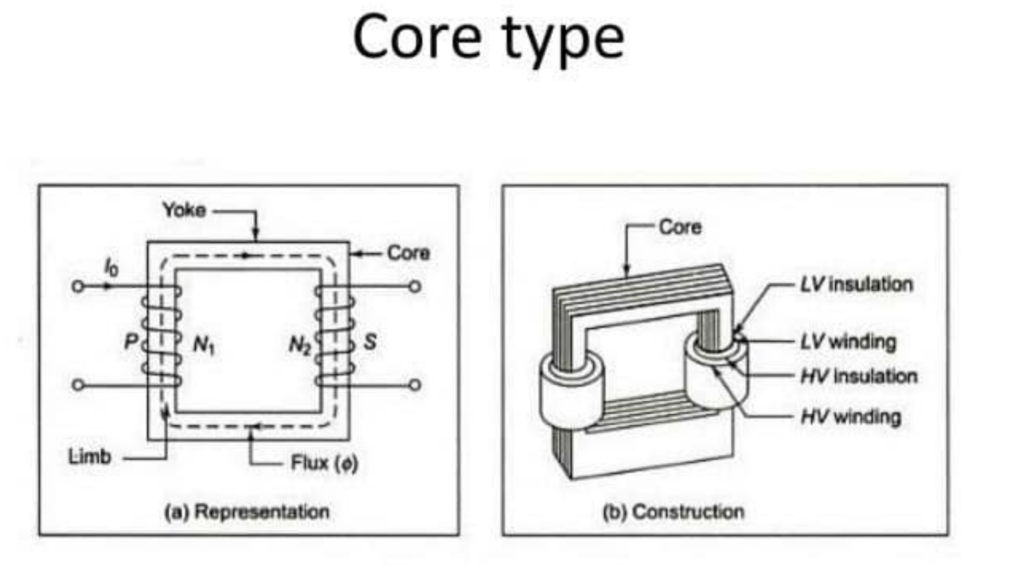
- Core – types transformer: features a laminated core with windings around two vertical legs, commonly used in power distribution.
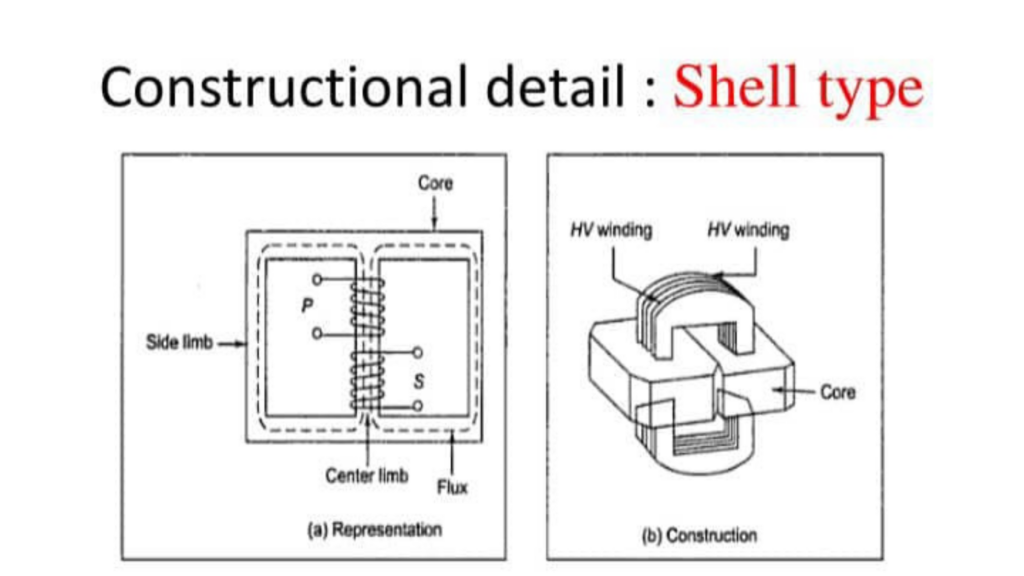
- Shell type transformer: has a central core with enclosed provided better short circuit protection and efficiency
- Based on Cooling system
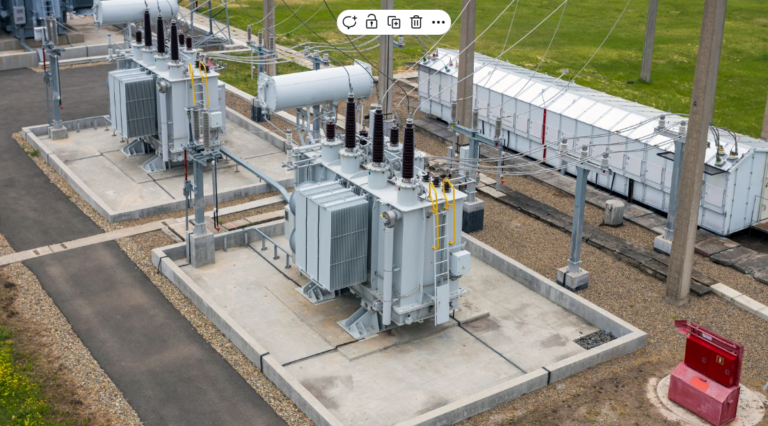
- Oil cooled transformer: uses transformer oil for insulation and heat dissipation common in large power system
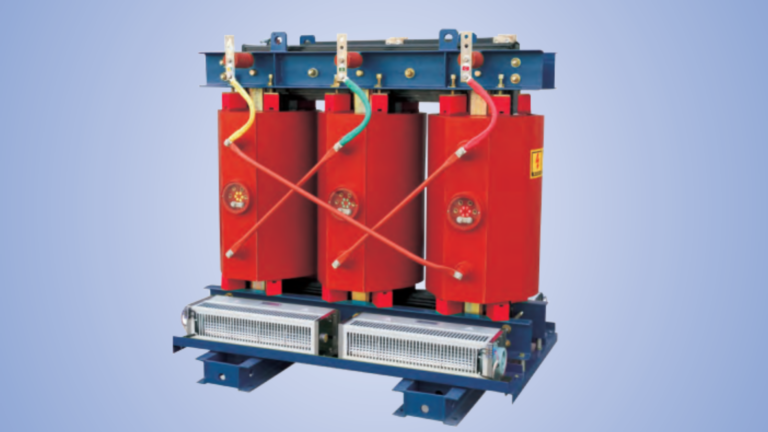
- Air cooled (Dry – types) Transformer: uses air for cooling suitable for indoor application with safety
Construction of power transformer
Power transformers are most essential components for electrical system used to step up or step down voltage levels for efficient transmission and distribution and their construction consists of several key parts designed for efficiency and safety.
- Core
- Windings
- Insulation system
- Cooling system
- Bushings
- Tap changer
- Transformer tank
- Conservator & breather (for –oil filled transformer)
- Protection and monitoring devices
Made from laminated silicon steel to minimize eddy current losses the core provides a low reluctance path for the magnetic flux constructed in different shapes such core type and shell type configuration
- Windings
Made of copper or aluminium conductor with high conductivity
there are two types
- Primary winding: connected to the input voltage source
- Secondary winding: delivers the transformed voltage
- Insulation system
Most of electrical insolation between winding and core but common insulation materials include paper, pressboard and mineral oil solid insulation (e.g. epoxy resin) by used electrical insulation in transformer due to its excellent insulating properties to heat and chemical and mechanical strength.
- Cooling system
Removes heat generated due to copper and iron losses.
Common cooling methods include:
Oil filled cooling (ONAN, ONAF) – uses mineral oil heat dissipation
- Air Cooling (AN, AF) found in dry type transformer
- Forced cooling (water or oil circulating system) used in large transformer
- Bushings
Provides insulated terminal for connecting the transformer to external circuits made of porcelain, resin or composite materials.
- Tap changer
Adjust voltage levels to compensate for variation in supply or load
- On load tap changer: adjust taps without interrupting the supply
- Off load tap changer: requires the transformer to be de- energized for adjustments.
- Transformer Tank
Houses the core and winding, filled with insulating oil for cooling and insulation made of steel, designed to withstand mechanical and thermal stress
- Conservator & breather (For oil –filled transformers)
- Conservator tank – allows oil expansion and contraction due to temperature changes
- Silica gel Breather: prevents moisture ingress maintaining and oil quality.
- Protection and monitoring devices
- Buncholz relay: detects gas accumulation due to internal faults
- Temperature sensor: monitor oil and winding temperature
- Pressure relief device: releases excess pressure in case of faults.
Power Transformers specifications
| N | Quantity | Value | Unit |
| 1 | Rated power | 40 | MVA |
| 2 | Rated frequency | 50 | HZ |
| 3 | Primary voltage | 66000 | V |
| 4 | Secondary voltage | 11000 | V |
| 5 | Rated primary current | 349.91 | Amp |
| 6 | Rated secondary current | 2099.46 | Amp |
| 7 | No. of primary turns | 1200 | Turn |
| 8 | No .of secondary turns | 200 | Turn |
| 9 | Primary winding resistance | 0.3365 | Ohm |
| 10 | Secondary winding resistance | 0.00831 | Ohm |
| 11 | Connection | Dyn1 | ——– |
| 12 | Temperature rise of oil | 65 | C |
| 13 | Total full load losses | 167 | KW |
| 14 | Impedance | 12.5 | % |
| 15 | Core cross section diameter | 560 | M.M |
| 16 | Cooling mode | ONAF | ——- |
| 17 | Ambient temperature | 30 | C |
| 18 | Top oil rise over ambient | 45 | C |
| 19 | Hot spot factor | 1.3 | ——- |
| 20 | Rated circuit breaker current primary side | 600 | Amp |
| 21 | Rated circuit breaker current secondary side | 2500 | Amp |
Applications of power transformer
Power generation and transmission
High voltage direct current (HVDC) system
Industrial application
Renewable energy system
Railway electrification
Commercial and residential power distribution
Data centres and it infrastructure
Hospitals
Oil and gas industry
Mining operation
Airports
Conclusion
Power transformer are essential part of electrical infrastructure enabling efficient voltage regulation transmission and distribution systems. they play a role in industries power plants and power supply as a demand for electricity continues to grow power transformers are energy efficiency grid stability and sustainable power solution with advancements in technology
FAQS
1. What is a power transformer used for?
A power transformer is used to step up and step down voltage in electrical transmission and distribution ensuring for more efficient power transfer over long distance
2. What is the difference between transformer and power transformer?
A transformer is a general term for voltage conversion devices, while power transformer specially refers to high capacity transformer used in power generation, transmission and distribution networks
What is a power transformer in a substation?
A power transformer in substation is high voltage transformer that adjust voltage levels for efficient electricity transmission and distribution with the grid
What is the main function of transformer?
The main function of power transformer is to convert levels while maintaining the same power for safe and efficient distribution
What is the principle of power transformer?
A power transformer operates on faradays law of electromagnetic induction where an alternating current in the primary winding generates a magnetic field inducing voltage in the secondary winding.




