Pad Mounted transformer : Complete Guide
Introduction
Pad mounted transformers are the quiet workhorses of power distribution: small, secured, and necessary for safely delivering electricity to homes, office buildings, and industrial environments. Whether you’re an electrical engineer, a facilities manager, or simply interested in the green metal box on the corner of the street or campus, you’ll benefit from this article.
In this article, we’ll explain what a pad mounted transformer is, how single-phase and three-phase pad mounted transformers are different, how to install them, and where you would use them. We won’t throw technical jargon at you. We’ll give you simple definitions, provide real world examples, and share insights from top manufacturers.
Let’s keep it simple – one phase at a time.
What is a Pad Mounted Transformer?

A pad mounted transformer is a ground mounted electric power distribution transformer placed in a tamper-proof, locked metal housing. A concrete pad supports the transformer, which is intended for outdoor installations in public or residential settings that prioritize safety and accessibility.
These units are safer than pole mounted transformers in urban areas because they eliminate dangerous overhead wires. They typically provide service for underground distribution systems using overhead distribution system designs; they perform the function of stepping down medium-voltage electricity (typically rated from 15kV to 35kV), and then distributing that same lower voltage electricity (120/240V).
How Does a Pad Mounted Transformer Work?
Pad-mounted transformers acquire medium-voltage power, fed through underground power cables. Inside, the transformer core and associated windings manage the reduction of voltage through electromagnetic induction and then output the electricity in usage-friendly lower voltages for homes and businesses.
The sealed nature of pad mounted transformers allows them to operate safely in open space outside, and many models use oil-filled or dry-type transformer cores to assist with insulation and cooling when in use.
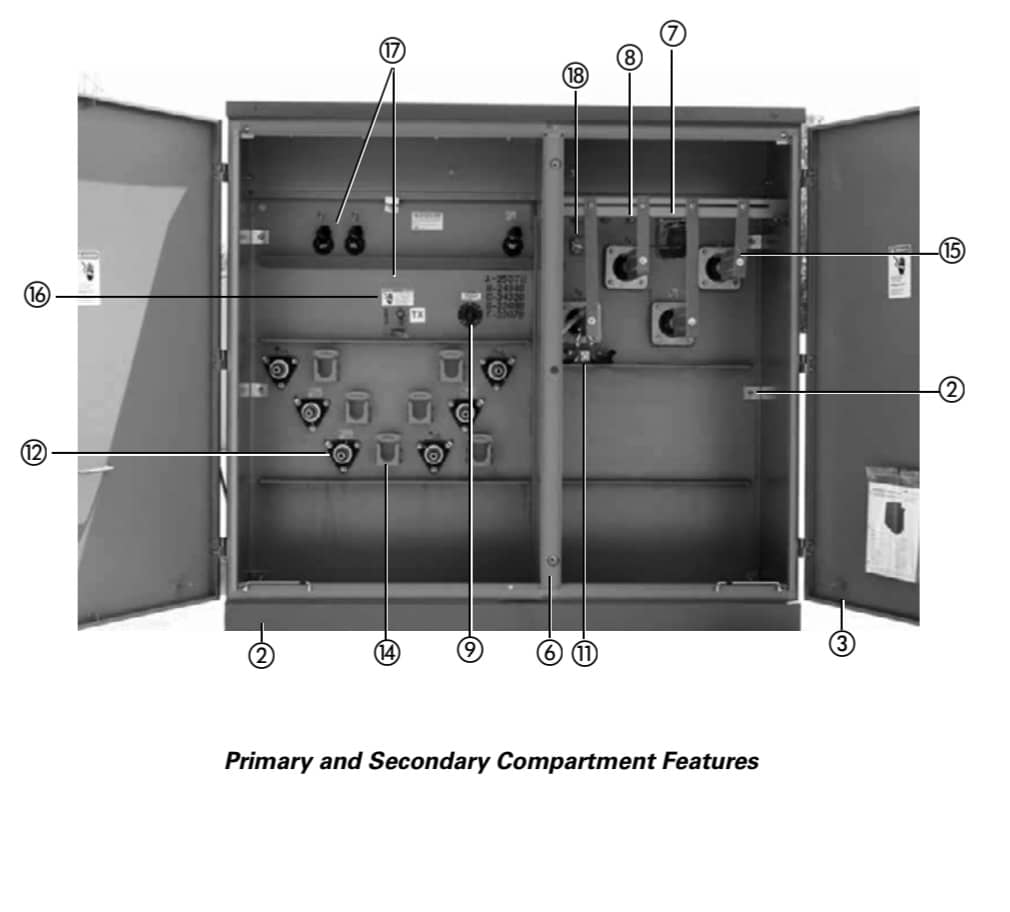
Components
According to Eaton and Maddox, the pad mounted transformer consists of the following basic components:
The primary and secondary bushings,
The primary high voltage fuses,
Load break switches,
Insulated windings,
Cooling fluid (usually mineral oil or FR3 fluid), and
Tamper-resistant housing.
Various Pad Mounted Transformers
Here are the most common types based on voltage and configuration:
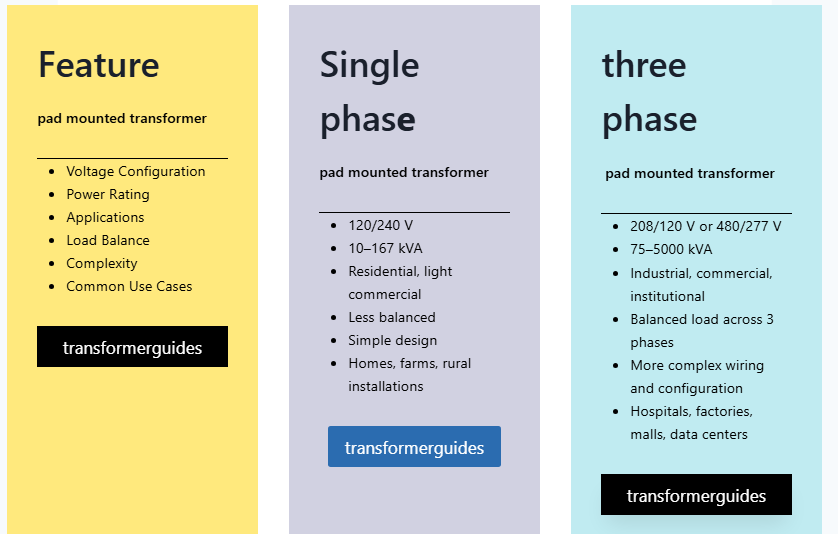
Single-Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
Intended for rural and residential areas
Typical ratings: 10 kVA to 167 kVA
Key players: Daeli m Transformer, Larson Electronics
Three-Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
Uses include industrial, commercial and utility-scale
Handles higher voltages and power
Available up to 5,000 kVA
High-quality pads from brands like Eaton, Hammond Power Solutions and Hitachi Energy
Typical Applications
Pad mounted transformers serve residential neighborhoods, shopping centers, hospitals, schools/universities, industrial complexes, suburban office parks and underground power systems.
Their tamper-resistant encasement makes them perfect for public settings.
Installation and Safety Tips
Franklin PUD states, Do not forget to maintain at least 10 feet clearance in front of the transformer. Do not plant too much of limbs/form plants/shrubs or fencing too close to the enclosure: it is an obstacle for access. Your kids can play anywhere except on top of or in direct proximity to the transformer box. Do not allow anyone to open or work on the unit except for professionals.
Clearance allows a utility crew to perform maintenance safely.
Comparison single phase and three phase pad mounted transformer
Applications
Pad mounted transformers are used in a variety of applications.
Residential Areas: Provide utility for neighborhoods powered by underground distribution systems.
Commercial Facilities: Power shopping centers, office buildings, and schools.
Industrial Complexes: Serve factories or manufacturing facilities that require substantial power.
Healthcare Facilities: Ensure that hospitals and clinics can perform reliably.
Data Centers: Ensure reliable power supply to critical infrastructure.
The small footprint and secure enclosure of the transformer makes it useful wherever space is limited and safety is a concern.
Installation and Safety Considerations
Proper installation and safety considerations for your pad mounted utility transformer.
Clearance: There should be at least 10 feet of clearance in front of the transformer to allow for maintenance and emergencies.
Accessibility: The transformer should be easily accessible for utility personnel.
Public Safety: As with all equipment, proper signage and educating the public is for public safety and to prevent tampering or playing in the vicinity of the transformer.
Vegetation: There should be no shrubs or trees around the transformer that may be a fire hazard or obstacles to service or maintenance.
Maintenance: Conduct routine visual checks of your transformer to assess for oil leaks, corrosion, or any damage.
Everyone’s overall safety is improved when we follow these procedures to minimize risks and help ensure the transformer lasts for a long period of time.
Leading Manufacturers
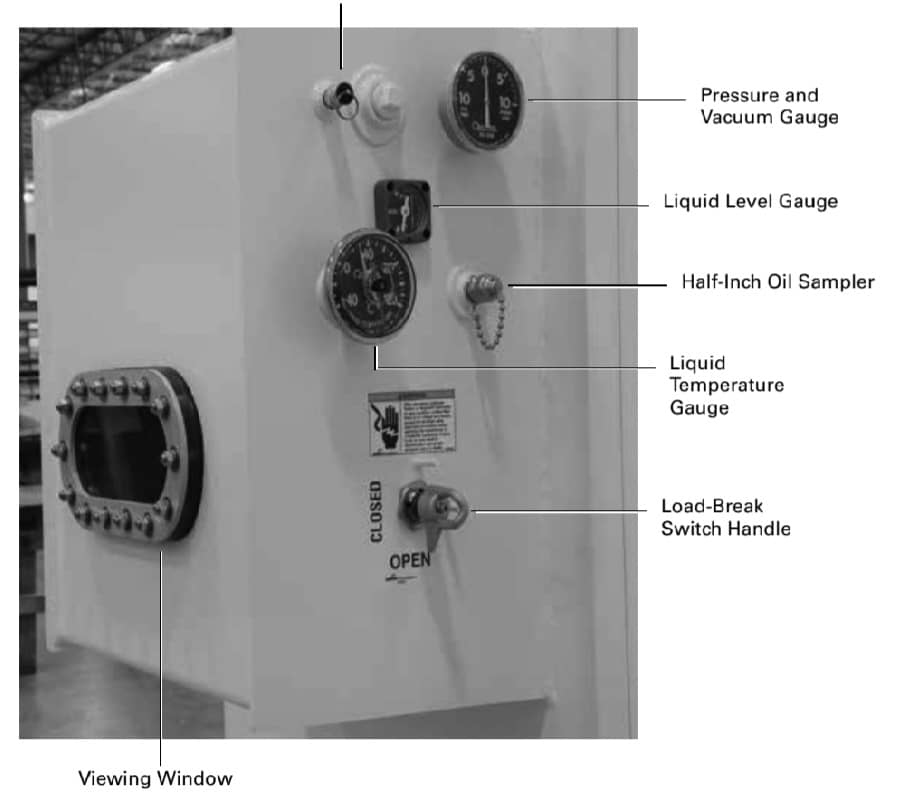
Some trusted manufacturers of pad-mounted transformers include:
Eaton: An excellent supplier of medium-voltage power distribution equipment.
Maddox: Supplies new and used transformers as well as transformers for specific applications.
Schneider Electric : Quality efficient and sustainable transformers, they provide good solutions to challenges.
Hitachi Energy: Seek their advanced transformer technologies for flexible applications.
Hammond Power Solutions: Good custom engineered transformer solutions.
Daelim Transformer – provides extensive lines of transformers that can be designed for your specifications.
If you obtain your transformer from a trusted and reputable manufacturer, you can be assured of quality, reliability, and conformance to industry standards.
Maintenance and Life
The service life of pad-mounted transformers can be increased with regular maintenance:
Oil testing: Periodic testing of the insulating oil helps to measure moisture and dielectric strength.
Component inspection: Fuses, bushings and/or gauges should all be checked for excess wear or damage.
Cleaning: Outside surfaces of transformers should be kept free of debris and contaminants to prevent corrosion.
Thermal imaging: vendors can provide infrared cameras for hot spots that could indicate problems.
With the right maintenance regime, pad-mounted transformers can work efficiently, for a life span of 20-30 years or longer.
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers are simply essential for power distribution today. They’re safe, reliable, and efficient for a variety of uses. Fully understanding the components, types, and maintenance of pad mounted transformers will allow them to run as intended, and for a long time. Pad mounted transformers are commonly used in electrical distribution infrastructure and with adherence to the installation and safety guidelines, partnering with a reputable manufacturer, and knowing its capabilities, it can be fundamentally seamless for stakeholders to include pad-mounted transformers in their electrical infrastructure.