Auto Transformer: Working, Types, & applications
What is an Auto Transformer?
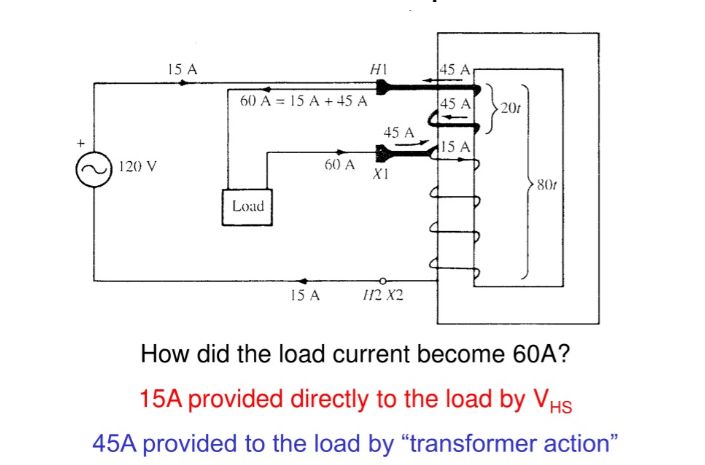
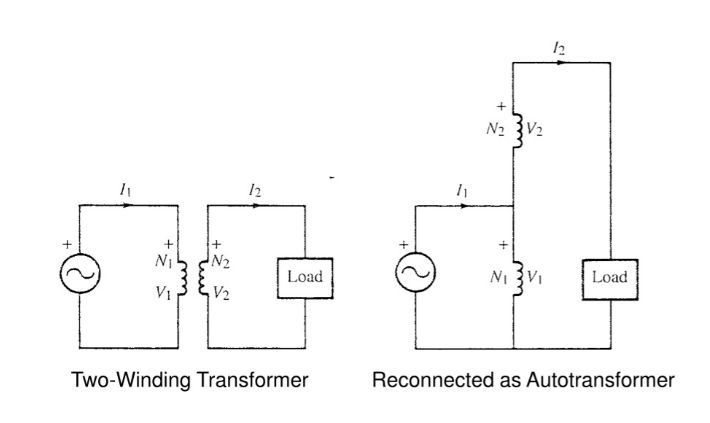
An auto transformer is a type of transformer that uses a single winding as both the primary and secondary winding. In contrast, in a traditional transformer, the primary and secondary winding are electrically isolated by separate coils, while an auto transformer shares some of the winding for both purposes.
Because of its configuration, an auto transformer can be made smaller, lighter, more efficient, and less expensive when a small voltage adjustment is required.
How Does an Auto Transformer Work?
The operating principle of an auto transformer follows Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. When an alternating (ac) current flows through the winding, it will create a magnetic field, and because of mutual and self-induction, a voltage is created due to the same winding.
To explain in simple terms:
A single coil is tapped at a certain point;
The portion from the tap to one end of the winding functions as the secondary winding (output);
The entire winding is the primary winding (input);
The tap point determines if the voltage is stepped up or down.
This configuration allows for variable output to the tap and is highly efficient regarding copper usage and power loss, while providing electrical isolation in some cases.
construction of an auto transformer
The construction of an auto transformer is much simpler than that of a conventional two-winding transformer. An auto transformer consists of a single continuous winding that serves as the primary and secondary circuits. The winding is wound around a laminated magnetic core, which concentrates the magnetizing flux. Laminations also reduce core losses (eddy currents and hysteresis). The core is made of laminated silicon steel to improve magnetic performance.
One of the main differences in construction is the taps in the winding at various locations, allowing for the adjustment of the secondary voltage. The tapped section of the winding acts as the secondary while the total coil acts as the primary. The winding was covered in high-quality insulation materials to ensure that the voltage differences along different areas of the same coil do not short-circuit or cause dielectric breakdown. The compact arrangement results in a transformer that is smaller, lighter, and less expensive than a conventional transformer.
Different Types of Auto Transformers
Auto transformers come in several configurations based on the application:
- Step-Up Auto Transformer
Is used to step voltage up from a lower level to a higher level. Usually found in power transmission applications. - Step-Down Auto Transformer
Is used to step voltage down, commonly found in domestic appliances and industrial equipment. - Variable Auto Transformer (Variac)
Provides a variable output voltage level. A device often found in testing labs and research facilities. - Three-Phase Auto Transformer
Used in three-phase power systems for large-scale voltage changing and motor starting.
Advantages of Auto Transformers
Auto transformers are often preferred over standard transformers. Here are some reasons why:
1. Efficiency
The quantity of copper and core material is reduced.
Lower resistive losses and core losses.
Efficiency is typically between 95% – 99%.
2. Space and Weight Savings
Less material used and a smaller footprint.
Easier to install and transport.
3. Cost Savings
Lower capital cost and lower maintenance costs.
Best for projects working with small voltage ranges and are on a limited budget.
4. Improved Voltage Regulation
Less voltage drop on full load due to less impedance and better magnetic coupling.
5. High Power Capability
For power applications, especially in the industrial environment.
Disadvantages of Auto Transformers
Despite their advantages, auto transformers are not effective in all situations.
- No Electrical Isolation
The primary can be affected by the conditions in the secondary side, because auto transformers do not isolate the primary from the secondary side, like two-winding transformers. This could be dangerous in sensitive applications. - Not Ideal for High Voltage Ratios
An auto transformer has only a small operating window of efficiency – the input voltage must be similar to the output. - Risk of Overheating
The thermal stress on a single winding in overload situations - Limited Fault Protection
Any fault on the secondary side, could negatively affect the primary circuit.
Applications of Auto Transformers
Auto transformers have many uses in a wide variety of fields due to their efficiency and compact design. Here are just a few commonly used applications:
- Power Transmission and Distribution
Stepping voltage levels up or down in HVAC (High Voltage AC) systems.
Electrical utilities also use auto transformers for voltage regulation and load balance - Industrial Applications
Starting induction motors at reduced voltage.
Starting motors supports a smoother control of current and torque during a motor startup. - Domestic Applications
Using auto transformers to correct voltage in refrigerators, air conditioning systems, and televisions in sections of the country with voltage variations. - Testing and Calibration
Laboratories and testing facilities use variances (Variable Auto Transformers) to create conditions for voltage tests or failures by simulating various voltage conditions.
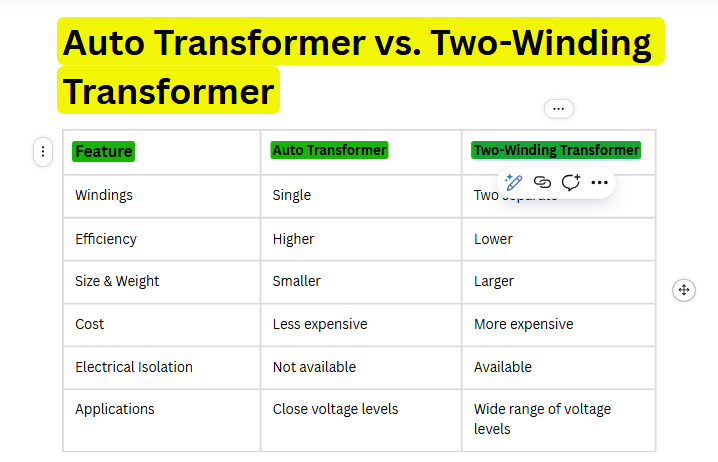
Auto Transformer vs Two Winding Transformer
conclusion
In conclusion, auto transformers are intelligent, compact, and efficient products ideal for applications where the amount of voltage variation is auxiliary and isolation is not a primary concern. Auto transformers are perfect for high power applications with little loss and therefore have considerable uses in power distribution, industrial applications, and everyday voltage correction.
Nevertheless, the lack of electrical isolation and limited voltage variation range should be considered when selecting an auto transformer. Always evaluate the requirements of your system and your safety expectations before installation.
FAQs
- What is the primary difference between an auto transformer and a traditional transformer?
An auto transformer uses one coil to create the primary and secondary sides, while a traditional transformer has two coils.
2. Are auto transformers safe?
Auto transformers are safe for the appropriate application but can pose a risk as they are not isolated electrically, which can be problematic in sensitive settings.
3. Can auto transformers be used for long distance power transmission?
While they can be used in transmission systems, they are more appropriately used for voltage regulation than covering long distances with high-ratio transformations.
4. What is a variac?
A variac is a type of variable auto transformer that allows a user to adjust the output voltage smoothly via a rotation knob.
5. Why are auto transformers more efficient?
They require less copper and core material to produce energy losses in the copper and iron, which give them higher efficiencies.