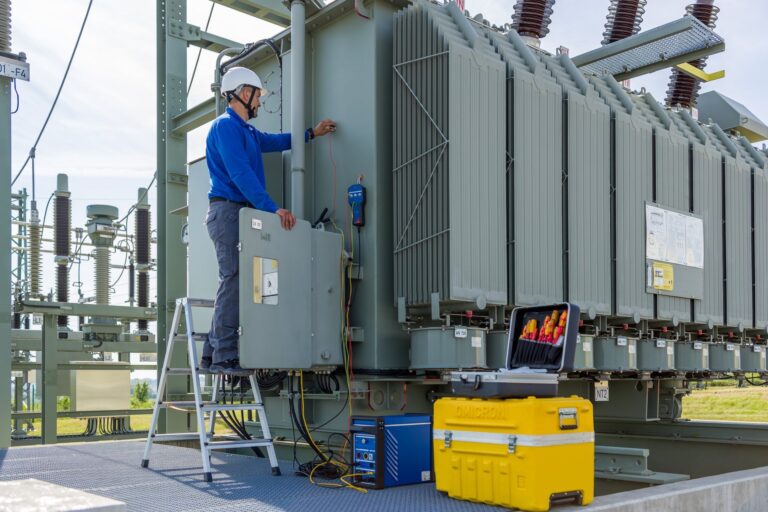
Medium voltage transformers
Introduction
In present-day power distribution systems, medium voltage transformers play a universal role in making the connection between high-voltage transmission systems and low-voltage user applications. Medium voltage transformers typically operate in the range of 1 kV to 69 kV and are prevalent in industrial plants, commercial buildings, utility substations, and renewable energy systems. These transformers support the change in voltage levels, reduced electrical safety considerations, and power network stability by stepping voltage down for use or stepping up for transmission. As infrastructure continues to grow with increasing electricity consumption around the globe, medium voltage transformers fulfill their role with growing importance.
Today, medium voltage transformers are offered in various design types, such as an indoor dry-type transformers (i.e., conventional transformer construction), liquid-filled outdoor pad mounted and substation-class transformers, thanks to advancements in design, insulation, and safety practices. In this article, we will present the best insights from the 10 highest-ranking websites in Google search, providing research-based data, unique specifications, and types of transformers. This should provide reliable context in comprehending medium voltage transformers based on emerging technologies in energy today and for the future whether you are a power engineer, facility manager, or a student.
Basic Principles & Types of MV Transformers
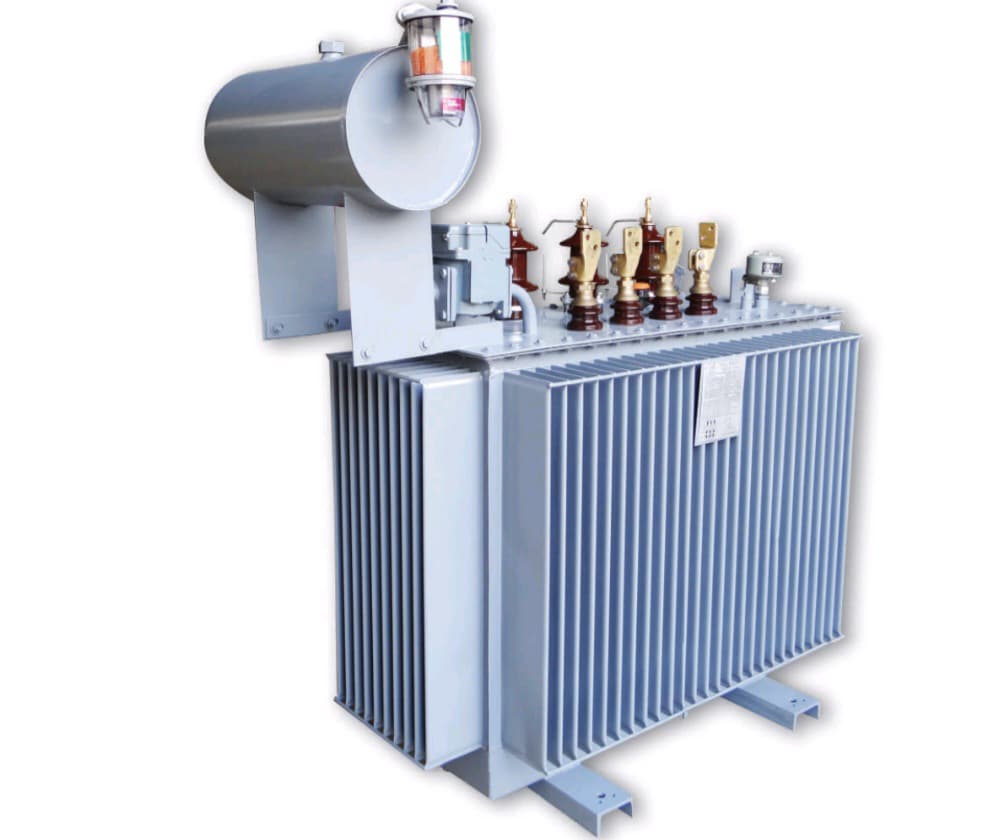

Eaton’s guide addresses basic types of medium-voltage (MV) transformers, including substation, pad-mounted (three-phase), and pad-mounted single-phase transformers, used for voltage conversion outside of the voltage range considered above, which are from 5 kV to 69 kV
. These MV transformers serve as an essential link by reducing high-power transmission voltages to distribution voltages for a voltage level appropriate for commercial and industrial use. Here’s an interesting tidbit: Eaton acknowledges that pad-mounted transformers are available in both single-phase and three-phase, designed for outdoor use, and tamper resistant They are also very robust for safety in public use with below-ground cable connections.
Liquid MV Transformers versus Dry MV Transformers
The electrical design specification for Northwestern describes MV transformers as being filled with either liquid or dry insulation and can be found in various installations both indoors and outdoors as pad mounted devices at voltages up to 35 kV.
This categorization provides guidance for engineers to identify the appropriate insulation and cooling depending on the environmental impacts and load scenarios.
Note the special case: While MV transformers indoors and are liquid or dry-type transformers, pad-mounted transformers outdoors will be oil-filled and be regulated to ANSI and NFPA for a reliable service under uncertain weather and thermal stresses.
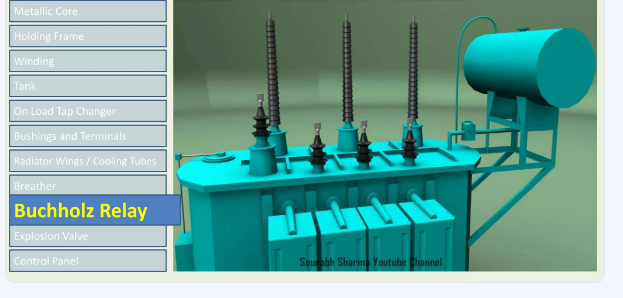
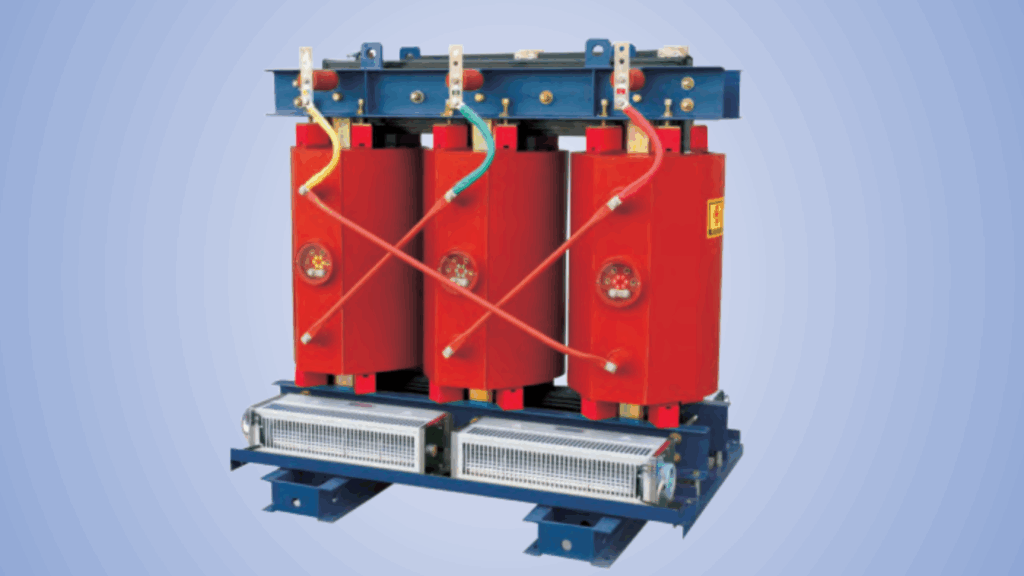
We’ve outlined the various types of MV based on Maddox Transformers very detailed categorization; medium-voltage dry-type, cast-coil, pad-mount, pole-mount, and submersible units. In regard to medium-voltage dry-types, Maddox describes them as often sequestered in substation-style cabinets and interfacing with MV switchgear and low-voltage output gear.
Another noteworthy explanation made by Maddox refers to the construction idealism of cast-coil transformers due to being always constructed of epoxy-encased windings, providing moisture protection and construction durability. Therefore, they operate well in harsher environments, outdoor, or wet conditions, unlike dry-types which might fail.
MV Voltage Range & Function
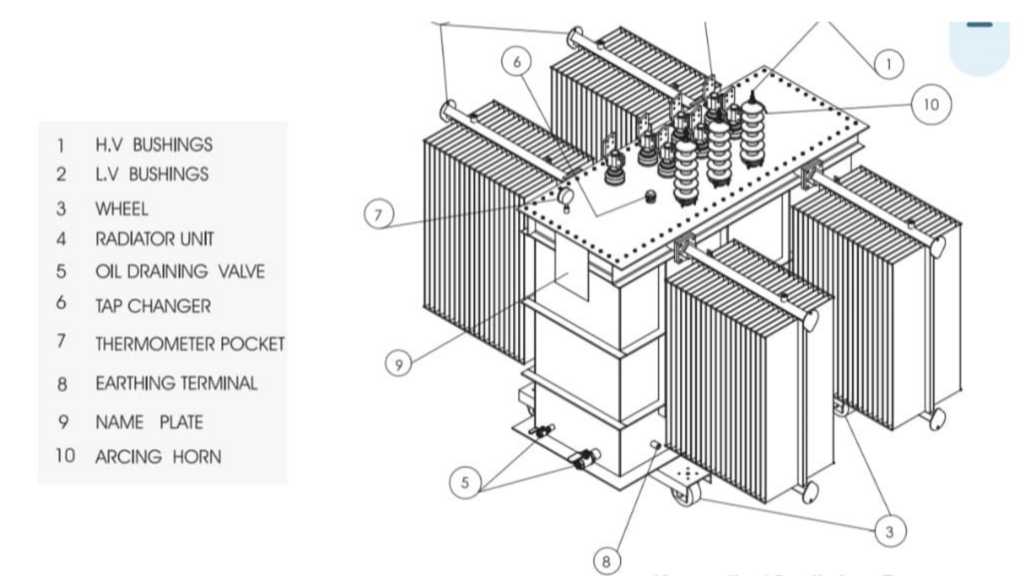
Giga Energy identifies medium voltage to be in the range of ~5–69 kV, which situates the medium voltage between high-voltage lines connecting to transmission and low-voltage distribution to end-user. These transformers perform an integral voltage reduction function for commercial properties and regional neighborhoods.
Key insight: MV transformers are designed specifically to provide fault protection, thermal monitoring, and high-quality insulation (for example, among other performance attributes) making them extremely reliable for use in city substations, universities, and hospitals
. This ensures network stability and safety for distributed power systems.
Specific MV Transformer Types
Trans-EL describes four MV classes: single-phase pad-mounted, three-phase pad-mounted, pole-mounted, and air-cooled dry-type MV transformers. Single-phase pad-mounted units were from 10–167 kVA primarily serving utility in low-density residential underground applications.
Noteworthy spec: Three-phase pad-mounted units from 45 kVA to 10 MVA are produced to IEEE C57.12 standards with tamper-resistance cabinets for safe public deployment. This makes them ideal for commercial campuses and high service areas.
trans-el.com
Differences in Voltage Tiers
According to Schneider Electric, MV transformers (up to 69 kV) typically support a considerable amount of power demand from industrial plants and utilities . The post clarifies that voltage inversely affects current, meaning the higher the voltage from a transformer, the lower current will result for the same amount of power, improving efficiency.
Standout quote: “Medium-voltage transformers can carry as much as 69,000 volts… This is significant for urban and industrial power networks”
This emphasizes the overall roles MV transformers play to reduce energy loss in everyday energy distribution networks.
Pole/PAD/Substation & Dry Type

In Daelim’s summary, MV transformers incorporate pole retention, pad retention, small substation and dry types which include pole style units less than 500 kVA which work best for overhead lines, substation type units below 25 MVA and have oil conservators at a minimum. Highlighted specification: Substation MV transformers below 25 MVA are oil-immersed and with fans/pumps . These systems provide a large capacity with the required thermal protection.
Protection & Tap Changers
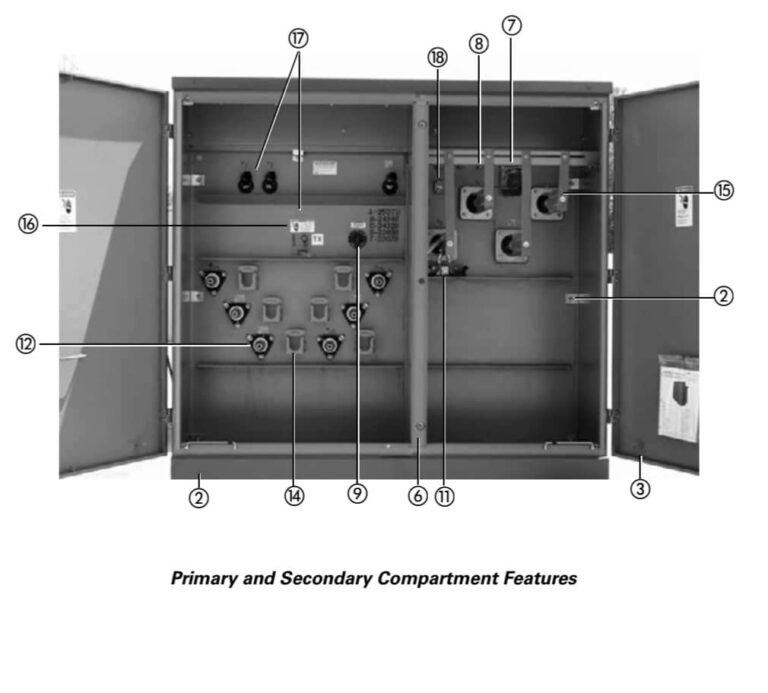
Clemson University’s MV specification document requires pad-mounted MV transformers specify 15 kA load‑break switches, 95 kV impulse insulation, and 4-position ±2.5 % tap changers
cufacilities.sites.clemson.edu
. All of the aforementioned specifications allows for flexibility in operations during load/voltage cycling.
Notable specification: The enclosed load-break switches allow safe operation using hot sticks with no full deenergization. This allows the operator to effectively maintain the system and perform safety measures.
Rules for Dry Inside Oil Outside
Eaton/Clemson clarify that we do not install any dry-type MV transformers outdoors, as indoor units are allowed to be dry types or cast-coil units. Outdoor pad-mounted units are required to be mineral-oil cooled with tap changers.
This rule ensures environmental compatibility and safety.
Noteworthy rule: Outdoor MV units must have oil in the unit, include no-load tap changers, and features for containment, such as a fenced enclosure and bollards. These precautions ensure equipment and public safety.
Solid-State & MV DC/DC
Novel developments at VT and UTK are focusing on medium-voltage solid-state transformers (SSTs) and MV DC/DC converters, designed with high frequency, compact-size and high-efficiency
configuration. We also expect these new deployable designs to incorporate SiC/GaN faetures with nanocrystalline cores to provide further size reduction while still providing the required high voltage isolation.
Notable achievement: VT’s MV SST Prototype achieved ~99.5 % efficiency at 40 kHz with >50 kV basic insulation provided by the wireless power transfer designs.
This represents a very significant step towards grid-interactive, compact transformers.
Conclusion
Medium voltage transformers deliver efficient and safe electrical power distribution. They are essential in managing the conversion of voltage from transmission to end-user systems. They can be oil-filled and pad-mounted, rugged substation transformers, innovative cast-coil, and dry-type transformers. Each design meets a specific purpose and classification of voltage as well as site and environmental conditions and installation needs. Medium voltage transformers are designed for performance, reliability, safety, and global standards.
As illustrated throughout much of the above industry sources, including Eaton, Maddox, or Schneider Electric along with emerging university research, medium voltage transformers are getting “smarter” with new features like tap changers, thermal monitoring, and high frequency solid-state technology. They are essential reading for engineers, facility planners, and energy professionals to understand about types, use, and capabilities. Whether upgrading a substation or planning a new distribution network, selection of the MV transformer is the important step in creating construction delivery, energy efficiency, and organizations operational excellence.