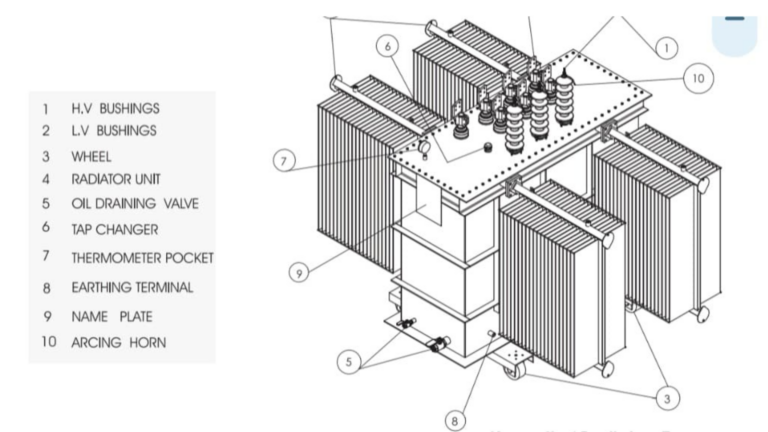
Difference between power transformer and distribution transformer
Table of Contents
introduction
transformers play is a vital role in electrical power system by stepping up and stepping down levels facilitate efficient of power transmission and distribution among the various types of transformers power transformers and distribution transformers are the most commonly used while both serve the purpose of transforming voltage their function design and operation characteristics different significant in this article we will explore the difference between power transformers and distribution in each details .
what is a transformer
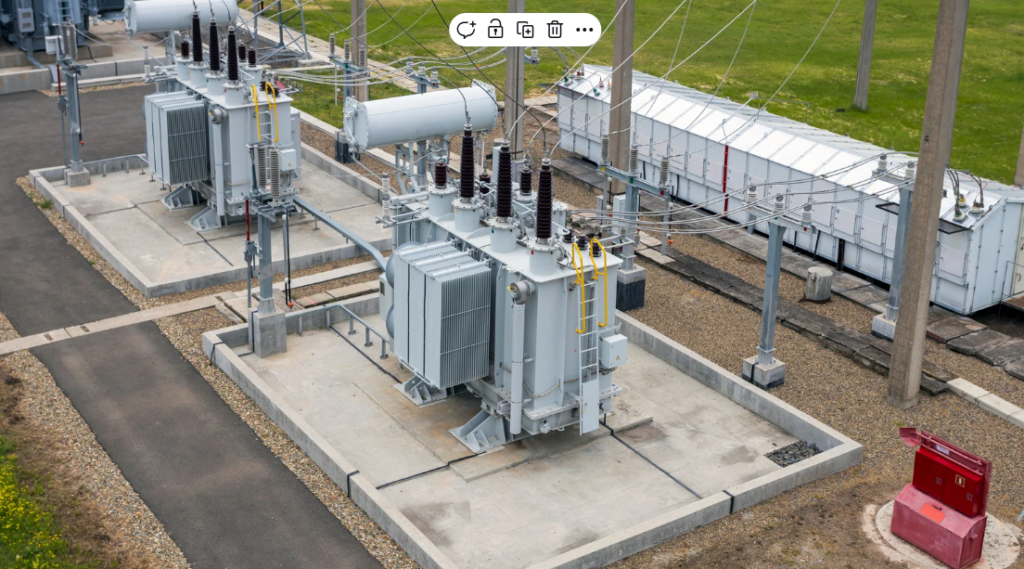

a transformer is electrical device that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction it consists of primary and secondary winding wrapped around a core and it work based on faradays low of electromagnetic induction . transformers are categorized based on their application , voltage levels and design with power transformers and distribution transformers being two major types
what is power transformer
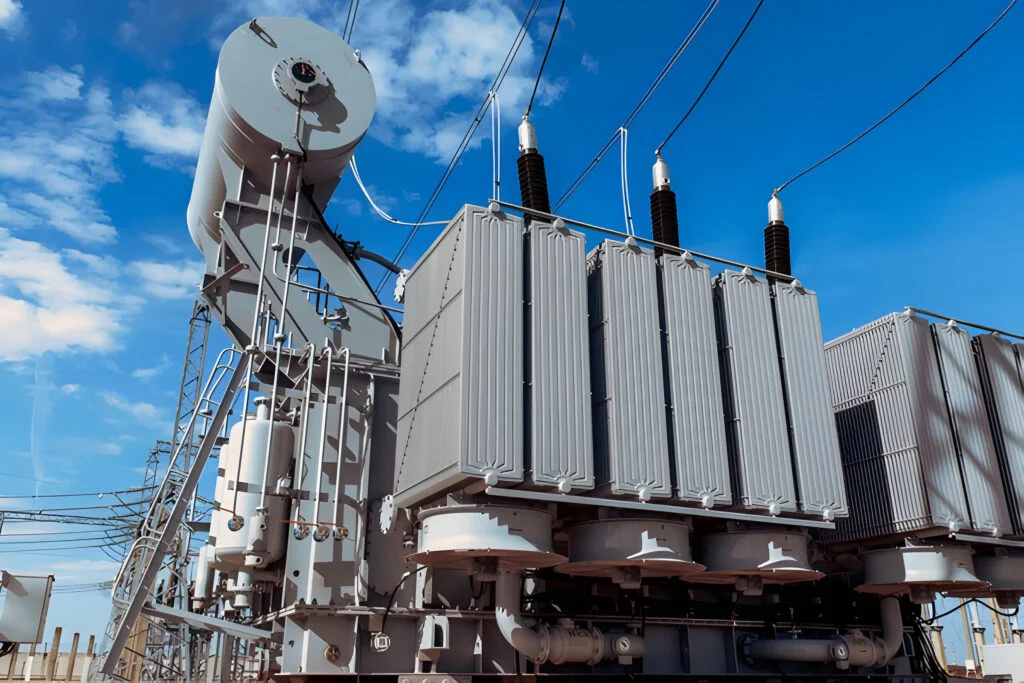

a power transformer is types of transformer primarily in high voltage transmission networks it is designed to handle large power loads efficiently and its usually found power generation station and substation
characteristics of power transformer
- high voltage rating : typically operates at voltage levels above 33KV
- large size : due to high power capacity these transformers are physically large and heavy
- continuous operation : works 24/7 at fully or near -full to measure stable power station
- high efficiency : design for maximum typically operating 75% load capacity
- cooling system : uses oil cooled or air cooled method to maintain temperature
- better insulation : built high quality insulation material to with stand extreme voltages
- conditions
where power transformers are used
- power plant, thermal , hydro , nuclear , solar, and wind power plant )
- transmission substation
- high voltage transmission network
- industrial and heavy manufacturing
Distribution transformer
a distribution transformer is transformer that steps down high transmission voltages to lower voltages suitable for local distribution to homes, commercial building and industries
characteristics of Distribution transformers
- lower voltage voltages rating: operates typically at voltage level below 33KV with common secondary voltages like 11KV, 6.6KV 440V, and 230 V
- compact size: smaller in size compared to power transformers for easier installation near load centres
- load fluctuation: operates with fluctuation loads, based on electricity demand in residential and commercial areas
- medium efficiency: works efficiently 50-70 % load capacity since power consumption varies through the day
- cooling system: can be oil cooled or dry types ( air cooled ) depending on the application
- short duty cycles : unlike power transformers these transformers operates for a shorter duration depending on the demand patterns
where distribution transformer is used?
residential
commercial building and offices
small and medium scale industries
street lighting system
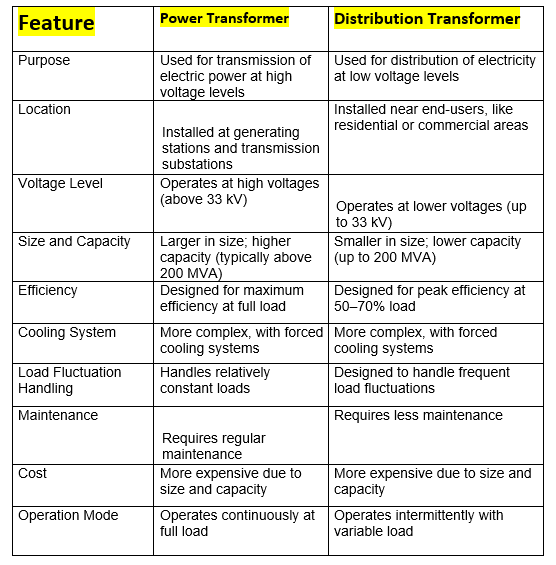
key different between power transforms and distribution transformers
the following table summarize the major differences
Difference between power transformer and distribution transformer
why these different matter
understand the differences between power transformer and distribution transformer is crucial fr electrical engineer utility companies and industries the selection of the right transformer depends on multiple factors like voltage levels, application and location
conclusion
both power transform and distributing are in defensible components of the electrical grid , power transformers are used in high voltage transmission system to efficiently transmit electricity over ling distance where distribution transformers step down voltage to deliver safe and suable for power to consumer . by understanding their function design and efficiency levels engineers and utility providers a can make informed deciding regarding the installation maintenance and selection of transformers for different applications
FAQs
1. why do power transformer operate at high efficiency ?
power transformers are design to run continuously at fault near full load optimizing their efficiency and minimizing losses in high voltage transmission
2. can distribution transformer be used in power stations?
no distribution transformers are design for lower voltages application and fluctuation load power require high capacity power for transmission purposes
3. what types of cooling is used in power and distribution transformers?
power transformers mainly use oil cooled or forced air cooled while distribution transformers can be either oil cooled or dry type air cooled
4. how long d power and distribution transformer last?
power transformers have lifespan typically 30 =40 years due to insulation and continuous operation where distribution last around 20 -30 years depending on load fluctuation usage
5. what happen if power transformer is overload?
overload a power transformer can lead to overheating insulation failure reduced efficiency and in server cases, transformer failure or fire hazard
6. are dry type transformers more suitable for indoor application?
yes, dry type distributions bare often used indoors in commercial building hospitals, and industrial facilities due to reduced risk and lower maintenance needs