Pole-mounted transformer
Table of Contents
Introduction
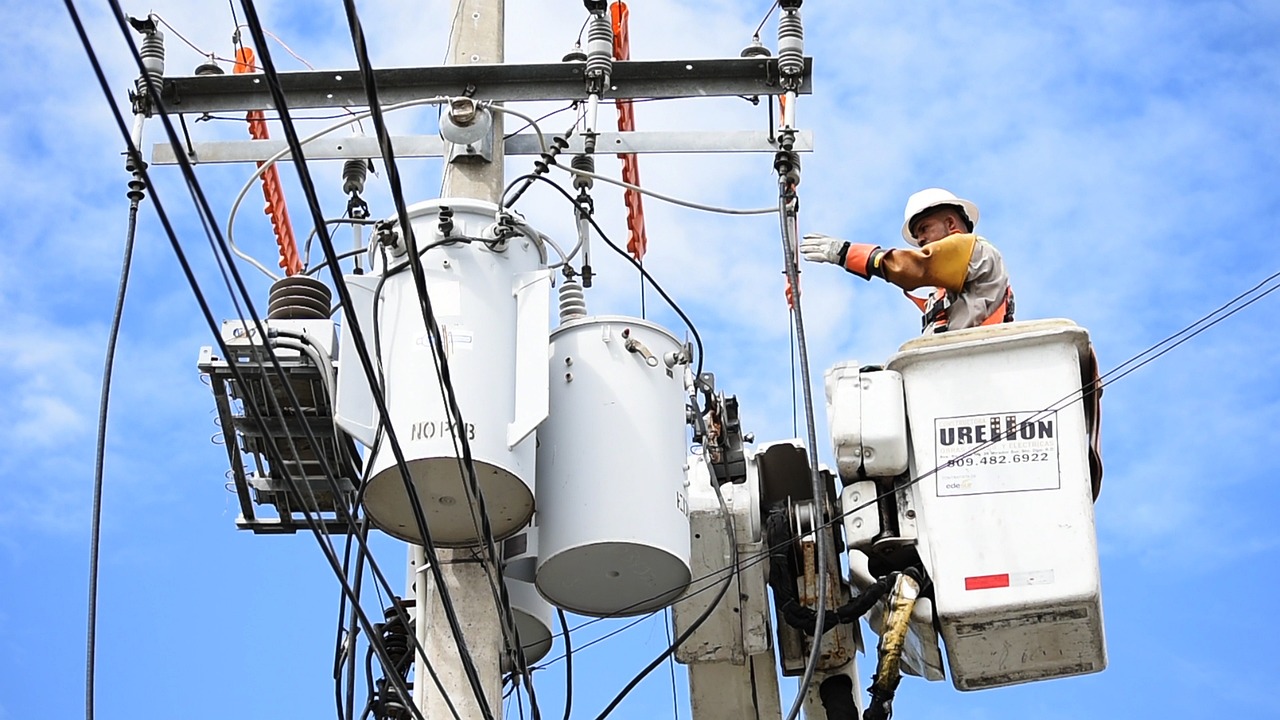
Pole-mounted transformers operate in the shadows, working as the central player in the electric distribution system. They take high voltage electricity from the high voltage power distribution pole mounted transformernetwork, and reduce the level of that voltage so that it is usable and safe for everyday consumption. Affordable, space efficient, and uncomplicated to install, pole-mounted transformers are sometime forgot in urban and rural installations within the electrical power networks but are a vital part of the overall power distribution system.
In this publication, we will discuss how pole-mounted transformers operate, the importance of pole-mounted transformers, and why they are the best choice in electrical power distribution systems. This document is suitable for engineers, contractors, or any interested bystander that ever wonders about the power lines above their heads.
What is a Pole Mounted Transformer?
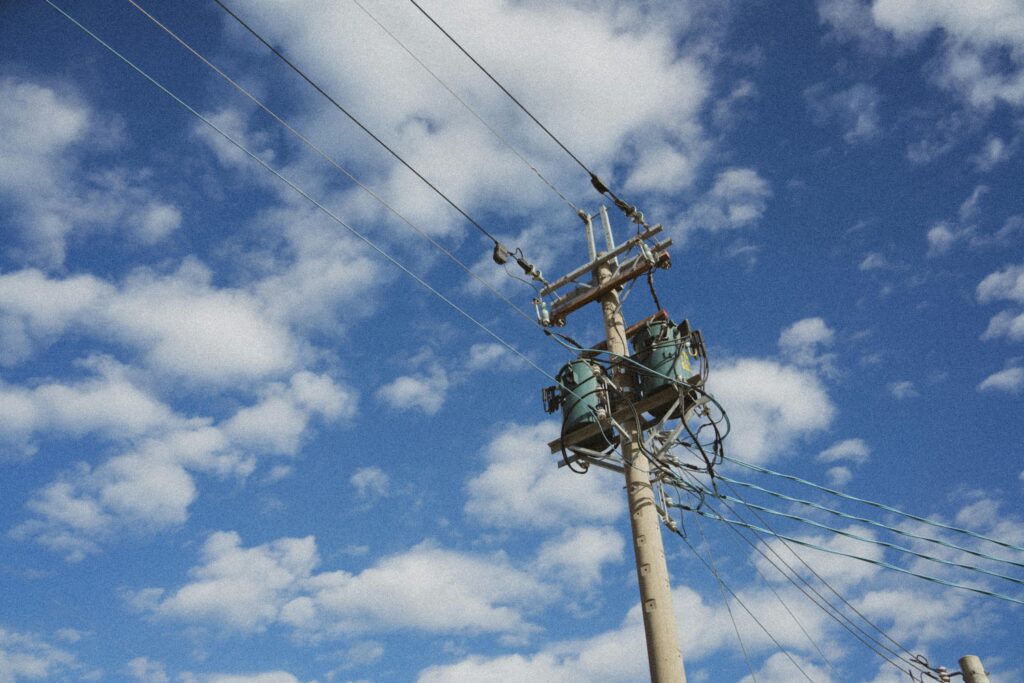

A pole mounted transformer is a transforming distribution transformer that is mounted on an electrical service pole. Typically used in overhead electrical distribution systems, they decrease high voltage electricity from the power grid to a usable lower voltage level for homes, and small businesses.. The pole mounted transformer is usually a cylindrical and rectangular shape unit mounted on a utility pole in residential or rural areas. These units are responsible for the final step of electrical energy distribution and are important to ensure electricity arrives safely and efficiently to the end user.
How Does a Pole Mounted Transformer Work?
How Does a Pole Mounted TraA pole mounted transformer converts high voltage electricity from the power grid into a lower, usable voltage power for homes and businesses utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a high voltage current passes into the primary winding of the transformer, it creates a magnetic field around a laminated iron core. The alternating current in the transformer primary creates an alternating magnetic field which is induced around the core. Then magnetic field induces a lower voltage in the secondary winding
of the transformer. The secondary winding coil has fewer turns of wire than the primary, thereby lowering the voltage (stepping it down) from, say, 11,000 volts (11 kV) to 415 volts or 240 volts, with a typical home having 240 volts. Once the voltage has been transformed, the lower voltage is distributed to nearby residential or commercial buildings. Pole mounted transformers are single-phase, mostly used in neighborhoods or three-phase, more common in commercial and industrial locations. Their efficiency, compactness, and ability to operate in different loading conditions distinctly identify them as a need in the last stage of power distribution.nsformer Work?
Types of Pole Mounted Transformers
Pole mounted transformers are categorized in a few different ways:
1. Based on Phase Single-phase transformers: Typically for smaller, residential loads Three-phase transformers: Typically for larger commercial or industrial loads
2. Based on Cooling t Oil-filled transformers: use mineral oil for cooling and insulation Dry-type transformers: use air for cooling; normally located at indoor or less accessible locations (usually not seen on poles)
3. Based on Mounting Conventional pole mounted: normally located on cross-arm or platform Compact pole mounted: compact designs that can be mounted in tightly spaced areas.
Advantages of Pole Mounted Transformers
Quick installation Mounting transformers on poles eliminates the costly and time-consuming excavation or construction work.
- Quick installation Mounting transformers on poles eliminates the costly and time-consuming excavation or construction work.
- Cost-effective Cost less to install and maintain than pad mounted or underground systems.
- Less risk of flood damage Pole mounted units are elevated and therefore, protected from potential water damage during flooding.
- Space-saving Ideal for urban or congested rural areas where the use of land is limited.
- Easier Fault Detection Fault Detection becomes easier and simple corrections can be made due to visible installation
Installing Pole Mounted Transformers
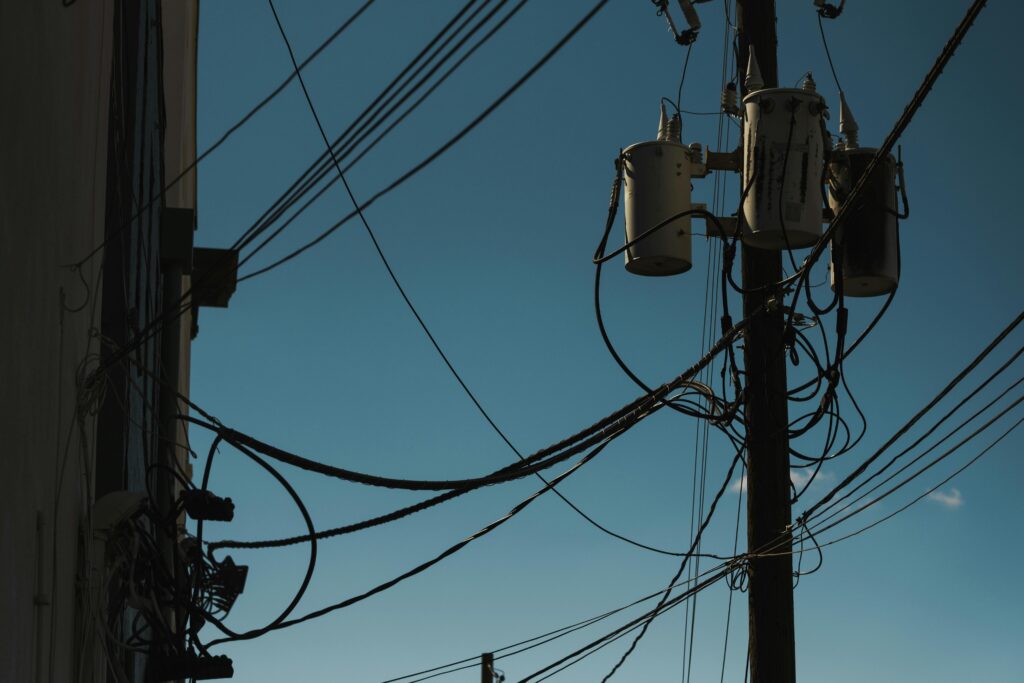

The installation is subject to the electrical regulations and safety procedures that govern your local installations. The following is a rough outline:
- Selecting the pole: Purposes dictate that the installation utilizes a pole that is adequately strong and tall in length, whether wood, concrete, or steel.
- Mounting hardware: Secure brackets and platform to the pole
- Mounting the transformer: The transformer is lifted using a crane or bucket truck and positioned onto the pole.
- Electrical connections: * Primary terminals are connected to high voltage service wires. * Secondary terminals are connected to low voltage service wires.
- Grounding: A ground wire is run from the pole mounted transformer to a grounding rod.
- Testing: The pole mounted transformer is tested for load, insulation, and proper operation before the unit is energized.
Common Applications
- Residential neighborhoods: The pole mounted transformer will typically step down utility electrical power to residential homes.
- Rural electrification: The pole-mounted transformer is an excellent choice for long distances between electric load and limited infrastructure.
- Agriculture: Powering irrigation pumps, barns, grain silos, and many more.
- Commercial applications: Powering small shops, community centers, etc…
- Temporary installations: Usage for situation requirements within a construction site providing electrical power wherever needed.
Maintenance Practices
- Visual Inspection –
- Check for anything that looks concerning– oil leaks, corrosion, loose connections, etc.
- Oil Level – For oil-filled transformers, confirm an adequate oil level and check for any moisture contamination.
- Load Check – Monitor the load levels to prevent overloading.
- Thermal Scan – Identify overheating issues early on.
- Grounding System Check – Confirms proper safety and performance.
Safety Issues
- Maintain Safe Distance – Always maintain a safe distance from the transformer.
- Insulated Tools – Only use approved insulated tools for any work around transformer
- Qualified Personnel – Any installation or service should be performed by licensed electricians or utility workers.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures – Always lock and tag out the possible conductive devices before performing maintenance
Environmental Considerations
Even though pole mounted transformers can provide benefits, they can have a detrimental impact on the environment if not treated correctly: Oil From Leaks – Leaks can cause soil and groundwater contamination. Environmental Noise – The humming sound can disturb residents in quiet residential neighborhoods. Unsightliness – Some residents may consider them an eyesore, especially in commonly searched beautiful rural areas. Environmental oil, quieter designs and possible location strategies are being used to combat these negative effects
Conclusion
Transformers mounted on poles are a vital part of contemporary power distribution networks. Their ability to be installed quickly, low cost, and efficiency make them very suitable for urban and rural applications. With the proper maintenance and safety practices, they can provide electrical service to thousands of homes and businesses across the globe.